Material
Every primitive flowing through a graph has a material property.
Here's an example:

Materials are particularly relevant for surface type primitives like PolyMesh and NURBS surface. But they are used for other purposes as well. The color channel of the material gives a NURBS curve its color, for example.
The material node modifies a primitive's material settings.
This is the graph that generated the rendering above:
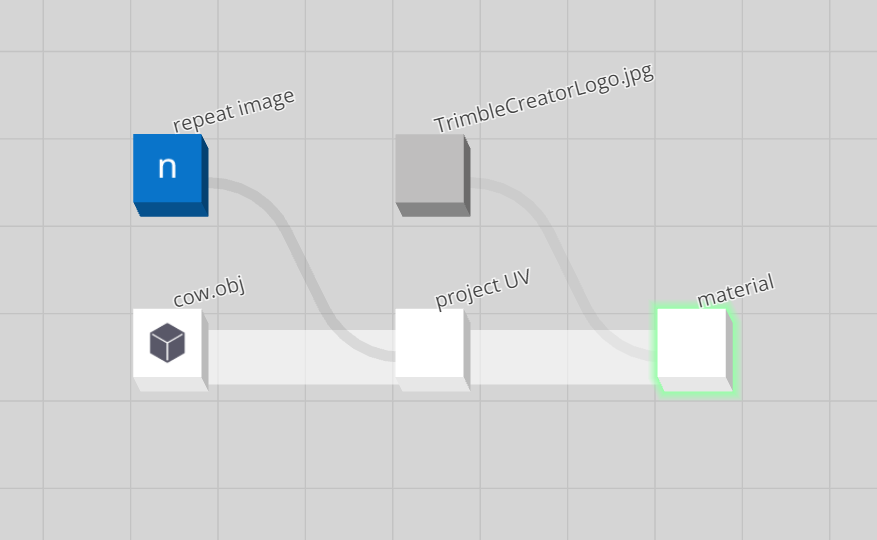
PBR Shading
Trimble Creator materials implement a metallic-roughness shading model. This type of shading is used in Physically Based Rendering (PBR) renderers.
For more on rendering, metallic-roughness shading and PBR, see the PBR shading guide from Adobe Substance.
Albedo
Albedo is the 'diffuse' or 'base' color of the primitive it is assigned to.
Albedo color can be varied across a surface using a texture.
The range of red, green and blue color values is 0 to 1 for the texture. These values can be multiplied with the provided color value. Resulting values above 1 are supported in PBR shading, and just indicate superbright colors.
Default is white.
Opacity
Opacity is the inverse of the transparency of the primitive it is assigned to.
- An opacity of 0 means the object is totally transparent.
- An opacity of 1 means the object is not transparent at all. This is the default.
Opacity can be varied across a surface using a texture. The texture overrides the provided opacity value.
Roughness
Roughness is an indication of how rough, smooth or 'diffuse' the primitive's surface is. It simulates microscopic imperfections (or lack thereof) of the surface.
Chalk is very rough. A glass window is not.
Roughness can be varied across a surface using a texture. Using a grayscale image is recommended.
Roughness value range is 0 to 1. Texture values can be multiplied using a provided multiplier value.
Default is 1 (fully rough, or diffuse).
Metallic
The metallic property is an indication of how much a primitive's surface acts like a metal.
Metallic can be varied across a surface using a texture. Using a grayscale image is recommended.
Metallic value range is 0 to 1. Texture values can be multiplied using a provided multiplier value.
Default is 0 (not metallic).
Reflectance
Reflectance is an indication of how reflective or 'specular' the primitive's surface is.
Reflectance can be varied across a surface using a texture. Using a grayscale image is recommended.
Reflectance value range is 0 to 1. Texture values can be multiplied using a provided multiplier value.
Default is 0 (not reflective, nor specular).
Bump
A bump map is used to simulate geometric detail on a surface it is applied to.
Bump requires a texture, and UV coordinates. The graph assumes the red channel of the texture will be used to perturb the normal as a derivative map. A derivative map uses a greyscale texture (or if a color image, the red channel thereof) to generate a normal map on-the-fly.
Bump value range is 0 to 1 for the texture, but can be multiplied using a provided multiplier value. Negative values will invert the bump details.
Default is 0 (no bump).
Incandescence
Incandescence or emissivity of an object is a color indicating how much a surface acts as a light. Even if nothing is lighting the scene, an emissive object will be visible.
Some renderers can use this property to make the object cast light into the scene.
Incandescence color can be varied across a surface using a texture.
The range of red, green and blue color values is 0 to 1 for the texture. These values can be multiplied with the provided color value. Resulting values above 1 are supported in PBR shading, and just indicate superbright emission color.
Default is black (no emission).
Double-sided
If switched off, the double-sided property is used to indicate to renderers that only one side of a primitive's surface should be rendered. The side the surface the normal is pointing out from.
Default is both sides. Note that many renderers assume single-sided is the default, causing a surface to become invisible from some viewing angles.
Texture size
This sizing factor is a multiplier on the primitive's UV coordinates. UV coordinates are required on the geometry primitives if textures are used for any of the above properties.
Default is 1 (no scaling).
Nodes
The material node modifies a primitive's material settings. The node can modify specific shading properties, and leave the other properties as-is. Multiple material nodes can be used in sequence to affect different shading aspects of primitives.
The set color node modifies a primitive's albedo color.
Textures
Textures are images used to 'map' certain shading properties, like base color, roughness, or bump. This allows for variation of the property across the surface of geometry primitives. Example: make only parts transparent, or reflective.
Import textures by uploading them. They can then be loaded into a graph using the image asset node.
To use them with materials, connect their asset uri output to the desired texture input of a material node.
UV mapping
Whenever a texture is used in a material to vary a shading property across a surface geometry primitive, that primitive needs to carry UV coordinates. This is so there is a map between pixels of the texture and 3D locations on the geometry's surface.
NURBS surface primitives carry UVs by design, but PolyMesh primitives sometimes need UVs to be added.
In general, this requires sophisticated UV mapping tools. This node provides basic ways of to applying UV coordinates onto PolyMesh primitives: project UV.